Human growth hormone produced by recombinant gene technology has been used extensively for anti-aging therapy during the past decade and more because of its ability to oppose maladaptive changes in body composition, particularly loss of lean body mass.
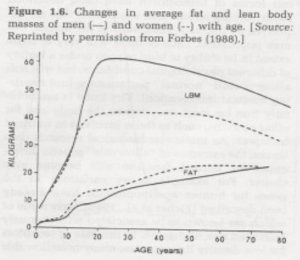
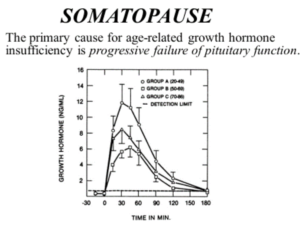
Lean body mass increases until the developmental program is completed at about age 20 – 22. Thereafter it declines slowly at first, but increases significantly in mid and later life. This decline is accompanied by a progressive increase in total and visceral body fat and metabolic changes that increase the risk for intrinsic diseases.
Muscle loss of aging partially attributable to reduced hGH
After combined exercise and hGH replacement therapy

Although effective in restoring certain youthful characteristics in aging subjects, hGH has certain medical and legal issues that sometimes restrict practitioners use of the product.
The major problems with hGH include:
• Improper dosing can lead to side effects that may be serious in some patients,
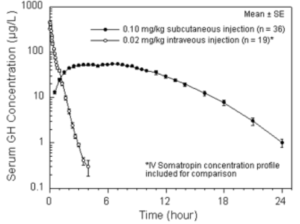
• Subcutaneous administration results in non-physiological or “square wave” exposure of tissues to hGH that is not controlled by normal feedback mechanisms and thus, eventually leads to tachyphylaxis and reduced efficacy,
The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) restricts the use of hGH in adults except for treatment of AIDS or human growth hormone deficiency (GHD) diagnosed according to specifically published guidelines.
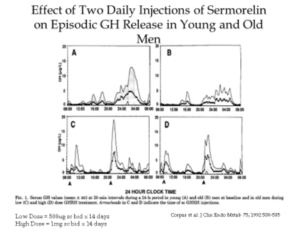
Based upon these potential problems with hGH, an alternative product that overcomes the medical and legal issues would be of significant value to anti-aging practitioners. The only such product currently available commercially is a structural analog of human growth hormone releasing hormone called growth hormone releasing factor (GRF) or SERMORELIN.

Unlike recombinant hGH which stimulates production of the bioactive hormone IGF-1 from the liver, GHRH/SERMORELIN simulates the patient’s own pituitary gland by binding to specific receptors that increase production and secretion of endogenous hGH.
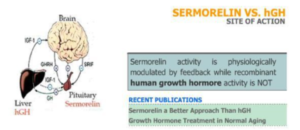
Sermorelin binds to and stimulates
hGH release directly from the pituitary
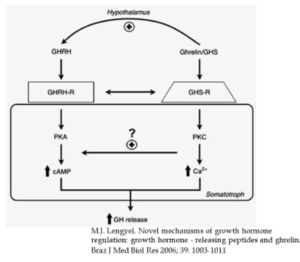
Because SERMORELIN increases endogenous hGH by stimulating the pituitary gland it has certain advantages over hGH that include:
Its effects are regulated at the level of the pituitary gland by negative feedback and by release of somatostatin so that over-doses of hGH are difficult if not impossible to achieve,
Tissue exposure to hGH released by the pituitary under the influence of SERMORELIN is episodic not “square wave” preventing tachphylaxis by mimicking normal physiology
By stimulating the pituitary it preserves more of the growth hormone neuroendocrine axis that is the first to fail during aging.
Pituitary recrudescence resulting from SERMORELIN blocks the cascade of hypophyseal hormone failure that occurs during aging thereby preserving not only youthful anatomy but also youthful physiology,
It provides the patient with all the benefits and more of hGH replacement therapy and furthermore, its OFF LABEL USE IS NOT PROHIBITED BY FEDERAL LAW.
Product Description and Dose Selection
Sermorelin: A better alternative to HGH
Sermorelin for injection is available in multi-dose vials containing sufficient product for 30 days of therapy. Each vial contains from 3 to 7.5 milligrams of Sermorlin as a sterile, lyophilized powder. Sufficient diluent (3 ml sterile, isotonic saline) is provided so that each 0.2 milliliter of the reconstituted solution contains daily doses ranging from 200 to 500 micrograms Sermorelin.
Recommended doses include the following:
3 mg MDV: 200 ug/day for men with BMI from 18.5 – 24.9
4.5 mg MDV: 300 ug/day for men with BMI between 25 and 29.9
6 mg MDV: 400 ug/day for women or for men with BMI between 25 and 29.9 7.5 mg MDV: 500ug/day for women or for men with BMI between 25 and 29.9
Initially these recommended dosages are based upon the results of clinical testing in men of normal weight in whom 200ug/day increased pituitary reserve of hGH (as indicated by enhanced responses to provocative testing) and increased IGF-1. A sample set of the latter data are provided in the following table. IGF-1 increased in men ranging in age from 50 to 66 years after 30 consecutive days SC administration of 200ug Sermorelin.
| Patient ID/Age | Baseline (ng/ml) | Interim Analysis (ng/ml) |
| BP/50 | 134 | 195 |
| DP/52 | 126 | 220 |
| JA/53 | 57.1 | 150 |
| LM/56 | 113 | 126 |
| RW/66 | 127 | 199 |
However, with expanded efficacy and safety studies and the physician/patient desire for more rapid and sustained effects on IGF-1 production and improved body composition, reasonable dosing has increased up to and including 1mg/day. In order to meet these increased demands for product, it is now available in 9 and 15 mg sterile vials. Additional formulations include adding GHRP-2 6mgs and 75mgs or Theanine. Please contact EC3Health for pricing on all Age management medications.




